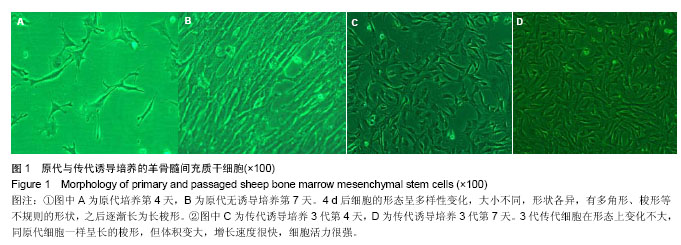
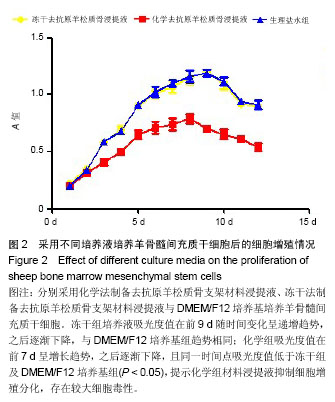
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (16): 2499-2505.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.16.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biocompatibility of freeze-dried antigen-extracted sheep cancellous bone scaffolds
Zhou Zheng1, Yang Ze-hui2, He Hui-yu2, Cui Jie2
- 1Department of Stomatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Prosthodontics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2014-03-01Online:2014-04-16Published:2014-04-16 -
Contact:He Hui-yu, Master’s supervisor, Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhou Zheng, Studying for master’s degree, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81060088
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Zheng, Yang Ze-hui, He Hui-yu, Cui Jie. Biocompatibility of freeze-dried antigen-extracted sheep cancellous bone scaffolds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2499-2505.
share this article

冻干组材料对羊骨髓间充质干细胞毒性很小,为0或1级,细胞相对增殖率均>90%,说明冷冻干燥羊松质骨支架材料没有细胞毒性;化学组开始没有毒性,但2 d以后细胞相对增殖率在58.04%-73.50%,材料毒性达到2级,说明其存在细胞毒性。 2.3 急性毒性实验 经过观察,冻干组材料浸提液注射过的兔在7 d内精神很好,饮食活动跟平常无差异,呼吸正常无运动减少等毒性反应;化学组材料浸提液注射过的兔短期内有轻度呼吸困难症状,3 h后症状消失;对照组在注射同剂量生理盐水后7 d内精神良好,饮食活动跟平常无差异。3 d内各组动物体质量均增加,通过方差分析检验3组动物体质量每天的平均增加差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表1。按照材料毒性的分级[12],冻干组材料无毒性,化学组浸提液有轻度毒性。"
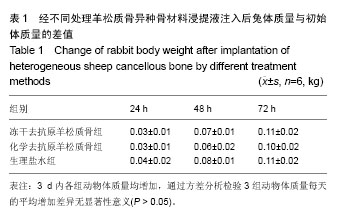

7 d后处死实验动物,随机抽取1只兔取肝、脾、肾作苏木精-伊红染色,经过观察各组肝、脾、肾苏木精-伊红染色片无异常(图3)。 2.4 热源实验结果 3组实验动物注射完各自材料浸提液及生理盐水后,冻干组和对照组动物在1,2,3 h三个时间段测得升高温度都<0.6 ℃,升高总数最高为0.85 ℃和0.7 ℃,亦达到国家标准(<1.4 ℃);化学组实验动物3个时间点测得的温度均>0.6 ℃,而且升高温度总和最高为2.45 ℃,未达到国家标准(<1.4 ℃);经过统计及方差分析,冻干组、对照组与化学组之间体温变化差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。 2.5 皮内刺激实验 冻干组在1,6,24,48,72 h观察背部皮肤没有明显的红斑、水肿及坏死,按照皮肤反应的评分系统得出APⅡ为0.37,为极轻微刺激;化学组在24 h及48 h时出现轻微红斑,按评分系统APⅡ为0.64,为轻度刺激;阴性对照APⅡ为0;阳性对照APⅡ为5.15,为重度刺激(表3)。"
| [1] Louis-Ugbo J,Murakami H,Kim HS,et al.Evidence of osteoinduction by Grafton demineralized bone matrix in nonhuman primate spinal fusion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(4):360-366; discussion Z1. [2] Athanasiou VT,Papachristou DJ,Panagopoulos A,et al.Histological comparison of autograft, allograft-DBM, xenograft, and synthetic grafts in a trabecular bone defect: an experimental study in rabbits.Med Sci Monit.2010;16(1): BR24-31. [3] Develioglu H,Unver Saraydin S,Kartal U.The bone-healing effect of a xenograft in a rat calvarial defect model.Dent Mater J.2009;28(4):396-400. [4] Park SA,Shin JW,Yang YI,et al.In vitro study of osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells on heat-treated porcine trabecular bone blocks. Biomaterials. 2004;25(3): 527-535. [5] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30. [6] 李罡,高春阳,金莲锦.异种脱蛋白松质骨支架与经诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(12):2217-2221. [7] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.GB/T 16886.5-2003.医疗器械生物学评价第5部分:体外细胞毒性试验[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2003:80-88. [8] 苏保,蒋电明,严永刚,等.氨基酸聚合物/硫酸钙生物工程骨的生物相容性研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(1):40-44. [9] 李国华,陈吉华.牙科全瓷材料3Y-TZP生物相容性初步评价[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(1):4-6. [10] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典2005版一部[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2005:附录66. [11] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.GB/T 16886. 10-2005刺激与迟发型超敏反应试验[S]//中华人民共和国国家标准医疗器械生物学评价.北京:中国标准出社, 2005: 8-13. [12] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.GB/T 16886. 11-1997医疗器械生物学评价第11部分:全身毒性试验[S].北京:中国标准出版社,1997:1-8. [13] Higetomi M,Doi K,Kuwata N,et al.Experimental study on vascularized bone allografts for reconstruction of mallive bone defecfs.Microsurgery.1994;15(9):663-670. [14] Tsuchia H,Hashimoto J,Crawford E,et al.Engineered allergenic mesenchymal stem cells repair femord segmental defect in rats.J Orthop Res.2003;1:44-62. [15] Orlowski TM,Godlewska E,Tarchalska M,et al.The influence of immune system stimulation on encapsulated islet graft survival.Arch Immunol Ther Exp(Warsz)2005;53(2):180-184. [16] Ni S,Chang J.In vitro degradation,bioactivity,and cytocompatibility of calcium silicate,dimagnesium silicate,and tricalcium phosphate bioceramics.J Biomater Appl. 2009; 24(2): 139-158. [17] Erdemli O,Captug O,Bilgili H,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation Of the effects of demineralized bone matrix or calcium sulfate addition to polycaprolactone bioglass composites.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(1):295-308. [18] Jahn K,Braunstein V,Furlong PI,et al.A rapid method for the Generation of uniform acellular bone explants.J Orthop Surg Res.2010;10(5):28-32. [19] 张富强.快速成型在生物医学工程中的应用[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2009:142-143. [20] 邢辉,陈晓明,张宏泉.骨组织工程支架材料[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2004,1(5):35-39. [21] Mastrogiacomo M,Muraglia A,Komlev V,et al.Tissue engineering of bone: search for a better scaffold.Orthod Craniofac Res.2005;8(4):277-284. [22] 郑磊,王前,裴国献.骨组织工程中细胞外基质材料的选择[J].中华外科杂志,2000,38(10):745-748. [23] Simon CG Jr,Khatri CA,Wight SA,et al. Preliminary report on the biocompatibility of a moldable, resorbable, composite bone graft consisting of calcium phosphate cement and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres.J Orthop Res.2002; 20(3):473-482. [24] Mastrogiacomo M,Papadimitropoulos A,Cedola A,et al.Engineering of bone using bone marrow stromal cells and a silicon-stabilized tricalcium phosphate bioceramic: evidence for a coupling between bone formation and scaffold resorption. Biomaterials. 2007;28(7):1376-1384. [25] Liu G,Zhao L,Zhang W,et al.Repair of goat tibial defects with bone marrow stromal cells and beta-tricalcium phosphate.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19(6):2367-2376. [26] Komlev VS,Peyrin F,Mastrogiacomo M,et al.Kinetics of in vivo bone deposition by bone marrow stromal cells into porous calcium phosphate scaffolds: an X-ray computed microtomography study.Tissue Eng.2006;12(12):3449-3458. [27] Papadimitropoulos A,Mastrogiacomo M,Peyrin F,et al.Kinetics of in vivo bone deposition by bone marrow stromal cells within a resorbable porous calcium phosphate scaffold: an X-ray computed microtomography study.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007; 98(1): 271-281. [28] Marcacci M,Kon E,Moukhachev V,et al.Stem cells associated with macroporous bioceramics for long bone repair: 6- to 7-year outcome of a pilot clinical study.Tissue Eng. 2007; 13(5):947-955. [29] Detsch R,Uhl F,Deisinger U,et al.3D-Cultivation of bone marrow stromal cells on hydroxyapatite scaffolds fabricated by dispense-plotting and negative mould technique.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19(4):1491-1496. [30] Oliveira JM,Rodrigues MT,Silva SS,et al.Novel hydroxyapatite/chitosan bilayered scaffold for osteochondral tissue-engineering applications: Scaffold design and its performance when seeded with goat bone marrow stromal cells.Biomaterials. 2006;27(36):6123-6137. [31] Tan KK,Tan GH,Shamsul BS,et al.Bone graft substitute using hydroxyapatite scaffold seeded with tissue engineered autologous osteoprogenitor cells in spinal fusion: early result in a sheep model.Med J Malaysia.2005;60 Suppl C:53-58. [32] Guo X,Zheng Q,Kulbatski I,et al.Bone regeneration with active angiogenesis by basic fibroblast growth factor gene transfected mesenchymal stem cells seeded on porous beta-TCP ceramic scaffolds.Biomed Mater.2006;1(3):93-99. [33] Schumacher M,Uhl F,Detsch R,et al.Static and dynamic cultivation of bone marrow stromal cells on biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds derived from an indirect rapid prototyping technique.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(11):3039-3848. [34] He Y,Zhang ZY,Zhu HG,et al.Experimental study on reconstruction of segmental mandible defects using tissue engineered bone combined bone marrow stromal cells with three-dimensional tricalcium phosphate.J Craniofac Surg. 2007; 18(4):800-805. [35] 周天健.一种牛骨衍生新型骨替代材料的脱脂处理[D].中南大学, 2010. [36] 田家亮,周宗科,廉永云,等.三种不同脱脂方法对猪骨脱脂的效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(16):3133-3136. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||